Effective Location Targeting in Google Keyword Planner
One of the most crucial elements of a successful keyword targeting is proper location targeting. What makes Google Keyword Planner such a powerful marketing tool is its ability to let you draw a precise boundary on a map around the area where you want to research your keywords’ effectiveness. This innovative feature was groundbreaking when it first launched and continues to be a top marketing tool today.
To structure your location targeting effectively in Google Keyword Planner, there are several key considerations. Read on to learn how to properly configure location targeting for your Google Ads campaign.
Structuring Your Location Targeting
Your options for location targeting, listed in descending order of general effectiveness, include: state, radius, city, zip code, and designated marketing area (DMA). Each of these targeting ranges has its own advantages and disadvantages.
In a recent project, a company’s roadside service runs along i69 and m53 in Michigan. I want to understand what users are searching for along those highways. This way we are using the words people most use in Google Search.
- State Targeting
Targeting an entire state is straightforward. You can set your Google Ads to target all locations within your state’s boundaries. This is usually the best option for smaller states. However, targeting a specific region within a larger state can be more complex. - Radius Targeting
The most effective way to target a specific area within a state is to use the radius targeting feature. By dropping a pin on the map in the Google Ads interface, you can define a radius around that point, whether you want to cover a few cities or an entire metro area. Radius targeting is typically easier and more accurate than targeting city by city or by zip code, which can sometimes hinder your campaign. - County Targeting
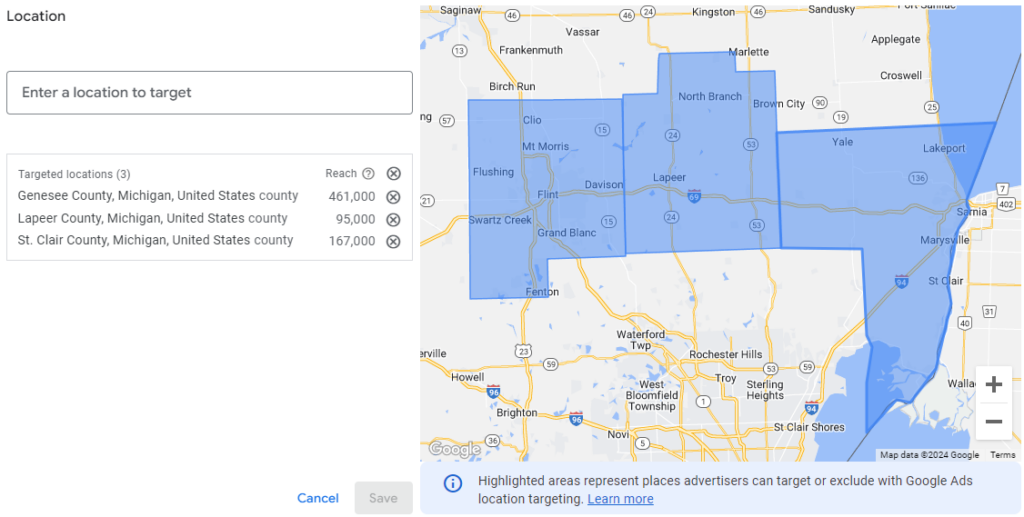
I find this to be the most effective for small businesses that offer a local service, but it really depends on your product or service. This is not as broad as a statewide analysis, but it’s not as focused as a zip code or neighborhood analysis. - City and Zip Code Targeting
Many business owners mistakenly believe that targeting specific zip codes is the most effective approach. In reality, zip codes can be geographically irregular. They may include areas you don’t want to service or exclude nearby areas you do. In densely populated metro areas, it can be challenging for Google to match users accurately to their zip codes.
If you need to target specific zip codes, the best approach is often to view these zip codes on a map and create a radius that encompasses most of them without being as restrictive as individual zip codes. This method typically improves ad visibility and ROI. - Designated Marketing Area (DMA) Targeting
It’s usually best to avoid targeting DMAs, as this can lead to your ads being shown to users far outside your desired service area. For example, targeting the Minneapolis-St. Paul DMA could result in your ads reaching users in northern Minnesota, far beyond your central metro area, potentially leading to unwanted leads.
Need Assistance with Location Targeting?
While there are numerous ways to target locations in Google Ads, targeting either an entire state or a specific radius usually proves most effective. Contact me today if you have further questions about proper location targeting and how it can help your business attract leads.



